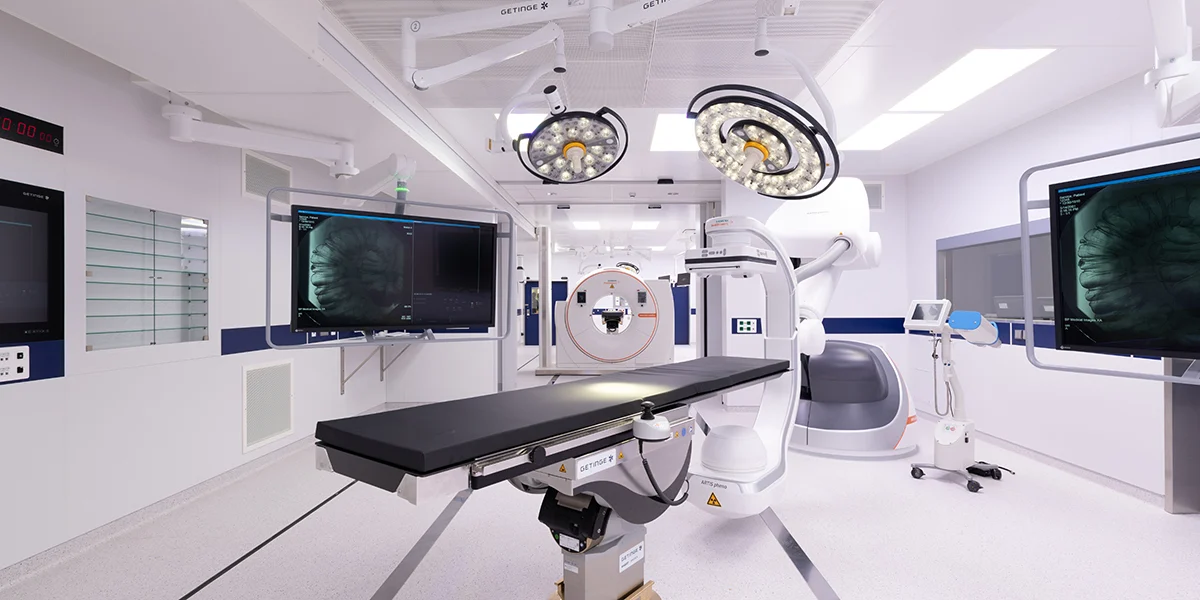
The operating room (OR) is the epicenter of medical procedures, where precision and efficiency are paramount. The continuous evolution of operating room equipment has played a pivotal role in enhancing surgical outcomes, improving patient safety, and facilitating the work of healthcare professionals. This article explores the diverse array of equipment found in modern operating rooms, the technological advancements driving their development, and the transformative impact on surgical practices across medical disciplines.
Surgical Table and Lights:
1. Surgical Tables:
The surgical table serves as the foundation of the operating room, providing a stable and adjustable platform for the patient during surgery. Modern surgical tables are designed with versatility in mind, allowing for easy adjustments to accommodate various surgical positions. Some tables are equipped with radiolucent tops, enabling X-rays and fluoroscopy during procedures, especially in orthopedic and neurosurgical interventions.
2. Operating Room Lights:
Proper illumination is crucial for surgeons to perform procedures with precision. Operating room lights, or surgical lights, have undergone significant advancements. LED lights now dominate the OR, offering bright and shadow-free illumination. These lights are adjustable in intensity and color temperature, providing optimal visibility and reducing eye strain for the surgical team.
Anesthesia Machines and Ventilators:
3. Anesthesia Machines:
Anesthesia machines play a vital role in administering controlled doses of anesthesia to patients during surgery. Modern machines offer a range of features, including integrated monitoring systems, touchscreen interfaces, and the capability to deliver a variety of anesthetic agents. Safety features, such as alarms for abnormal vital signs, contribute to the secure administration of anesthesia.
4. Ventilators:
Ventilators are crucial in maintaining a patient’s respiratory function during surgery, particularly under general anesthesia. Advances in ventilator technology have led to more precise control over ventilation parameters, adaptive support modes, and improved patient monitoring. These enhancements contribute to better patient outcomes and reduced complications.
Surgical Imaging Systems:
5. C-Arm Fluoroscopy Machines:
C-arm fluoroscopy machines are essential in various surgical specialties, including orthopedics, cardiology, and vascular surgery. These machines provide real-time X-ray imaging, allowing surgeons to visualize the placement of implants, guide catheters, and perform minimally invasive procedures. The flexibility of C-arm positioning enhances their utility across a range of surgical disciplines.
6. Intraoperative MRI and CT Scanners:
Some advanced operating rooms are equipped with intraoperative MRI and CT scanners, enabling real-time imaging during surgery. These systems allow surgeons to assess the progress of procedures, confirm the accuracy of interventions, and make immediate adjustments if necessary. Intraoperative imaging contributes to improved precision and patient safety.
Electrosurgical Units and Laser Systems:
7. Electrosurgical Units:
Electrosurgery involves the use of high-frequency electrical currents for cutting, coagulating, and dissecting tissues. Electrosurgical units have evolved to offer precise energy delivery, various modes for different surgical tasks, and enhanced safety features. These units contribute to reduced bleeding and tissue damage, particularly in minimally invasive procedures.
8. Laser Systems:
Laser technology has found applications in various surgical specialties, including ophthalmology, dermatology, and urology. Laser systems in the operating room provide precise cutting and ablation capabilities. They are employed in procedures such as laser eye surgery, skin resurfacing, and the treatment of kidney stones. Advances in laser technology continue to expand their utility in surgical settings.
Robotic Surgical Systems:
9. Robotic Surgical Systems:
Robotic-assisted surgery has emerged as a transformative force in the operating room. Robotic systems, such as the da Vinci Surgical System, enable surgeons to perform minimally invasive procedures with enhanced precision and dexterity. These systems feature robotic arms controlled by the surgeon, offering 3D visualization and wristed instrument movements. The integration of robotics has revolutionized procedures in urology, gynecology, and general surgery.
Challenges and Considerations:
While operating room equipment has undergone remarkable advancements, challenges and considerations persist:
1. Integration and Compatibility:
The integration of diverse technologies in the operating room can pose challenges related to compatibility and interoperability. Ensuring that different equipment seamlessly works together is crucial for a smooth workflow and optimal patient care.
2. Training and Familiarity:
Healthcare professionals must undergo comprehensive training to become proficient in using advanced operating room equipment. Familiarity with new technologies is essential to maximize their benefits and minimize the risk of errors.
3. Maintenance and Upkeep:
Regular maintenance and calibration of equipment are essential to ensure their reliability and accuracy. Healthcare facilities must invest in robust maintenance programs to prevent equipment malfunctions and downtime during critical procedures.
Future Trends and Innovations:
The future of operating room equipment holds exciting possibilities with ongoing research and development. Anticipated trends include:
1. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR):
The integration of AR and VR technologies in the operating room is poised to enhance surgical planning and visualization. Surgeons may use AR to overlay digital information on the patient’s anatomy during procedures, providing real-time guidance and insights.
2. Artificial Intelligence (AI):
AI applications in the operating room are expected to expand, assisting surgeons in decision-making, analyzing imaging data, and predicting patient outcomes. AI algorithms may contribute to personalized treatment plans and improved surgical precision.
3. Telepresence Surgery:
Advances in connectivity may lead to the development of telepresence surgery, where surgeons can remotely control robotic systems to perform surgeries across geographical distances. This could improve access to specialized surgical expertise in remote or underserved areas.
Conclusion:
Operating room equipment has undergone a remarkable transformation, evolving from basic tools to sophisticated systems that redefine the possibilities of surgery. The integration of advanced technologies, such as robotics, imaging, and artificial intelligence, continues to shape the future of the operating room, offering unprecedented precision, safety, and efficiency. As the healthcare landscape progresses, the ongoing collaboration between medical professionals, engineers, and researchers will undoubtedly lead to further innovations, ultimately improving patient outcomes and redefining the boundaries of what is achievable in the operating room.
